Web3 (also known as Web 3.0) refers to the next evolution of the internet that incorporates concepts such as decentralization, blockchain technology, and token-based economics. While still an emerging technology, many believe Web3 will revolutionize how we interact online and disrupt many digital industries. This guide provides an in-depth look at what Web3 is, its key components, and its potential impacts.
Contents
- 1 Overview of Web3
- 2 What are Web1 and Web2?
- 3 What technologies support Web3?
- 4 How is Web3 different from Web2?
- 5 Key Components of Web3
- 6 Key Benefits of Web3
- 7 What are some examples of Web3 in the real world?
- 8 Challenges Facing Web3 Adoption
- 9 Examples of Popular Web3 Applications
- 10 The Evolution of Web3
- 11 What are some concerns around Web3?
- 12 Frequently Asked Questions About Web3
- 12.1 Is Web3 the same as blockchain?
- 12.2 Is Web3 already here?
- 12.3 Do I need to buy cryptocurrencies to use Web3?
- 12.4 Is Web3 going to replace the internet?
- 12.5 Does Web3 have security risks?
- 12.6 What will Web3 disruption look like?
- 12.7 Who will regulate Web3?
- 12.8 Is Web3 too complex for average internet users?
- 13 Conclusion
Overview of Web3
At a high level, Web3 aims to create a new iteration of the internet that is:
- Decentralized – Power and control are distributed, not concentrated in the hands of a few companies
- Open – Built on open-source protocols and software that anyone can use to build compatible applications
- User-centric – Users have ownership over their data and platform interactions
- Transparent – Transactions and interactions can be viewed publicly on the blockchain
This differs greatly from today’s internet (Web2) that is dominated by major tech platforms like Google, Facebook, and Amazon. Under the current model, these companies control most online activity from data to infrastructure.
Web3 shifts power back to individuals users through concepts like blockchain, cryptocurrency wallets, decentralized apps (dApps), decentralized storage systems, and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). The result is an internet that is more secure, private, censorship-resistant, and peer-to-peer.
What are Web1 and Web2?
Web1 and Web2 refer to previous eras of the internet’s evolution:
Web1 (1980s – mid 1990s)
- Read-only, static web pages
- Very limited interactivity
- Early search engines and information portals
- Individuals mainly consumed rather than created content
Web2 (mid 1990s – present)
- Dynamic web applications
- Rise of social media, user-generated content, mobile apps
- Dominated by major centralized platforms like Google, Facebook, Amazon
- Huge amounts of data generated and monetized
- Shift towards user participation and interactivity
Web3 aims to build on Web2’s participatory aspects while decentralizing power away from big tech’s dominance over data, platforms, and economics. But it incorporates many of the technical innovations from the Web2 era like cloud computing and mobile access.
The evolution shows how the internet has progressively become more interactive, social, and decentralized from its initial roots as a read-only information network. Web3 represents the next stage in this evolution to create an internet that is open, transparent, interoperable, and user-owned.
What technologies support Web3?
Here are some of the key technologies that enable and support the development of Web3:
- Blockchain platforms – Such as Ethereum, Solana, Polkadot, Cosmos, etc. They provide the decentralized infrastructure for applications.
- Cryptocurrency protocols – Allow for creation and exchange of digital assets and currencies like Bitcoin, Ether, USDC.
- Decentralized storage – Filecoin, IPFS, Storj, Arweave enable distributed data storage.
- Decentralized identifiers (DIDs) – Enable user identity and data ownership without central authorities.
- Zero knowledge proofs – Allow validation of data without revealing contents, enhancing privacy.
- Oracles – Chainlink and others provide external data to blockchains.
- Layer 2 scaling – Solutions like Arbitrum and Optimism allow more complex dApps.
- Sidechains – Allow assets and data to be transferred between different blockchains.
- Decentralized cloud services – Provide computing resources like Dfinity and iEx.ec.
- Mesh networks – Allow peer-to-peer connectivity without ISPs like Althea Mesh.
- Crypto wallets – Enable users to safely access Web3 with non-custodial wallets.
- Decentralized VPNs – Encrypt network traffic without relying on VPN intermediaries.
- Virtual worlds – Web3-enabled metaverse platforms like Decentraland and The Sandbox.
This mix of protocols, infrastructure, and services collectively enable the decentralized web vision of Web3 to be realized.
How is Web3 different from Web2?
The core difference between Web2 and Web3 is the shift from centralized to decentralized control. In Web2, a few dominant platforms like Google, Facebook, and Amazon act as intermediaries that Web users must go through to access content and services. These companies centralize power and value creation.
Web3 utilizes new technologies like blockchain, cryptocurrency, and decentralized apps to remove intermediaries. Value accrues to networks of users rather than centralized platforms. Content, identity, payments, and infrastructure become open, transparent, and user-governed rather than controlled by corporate gatekeepers.
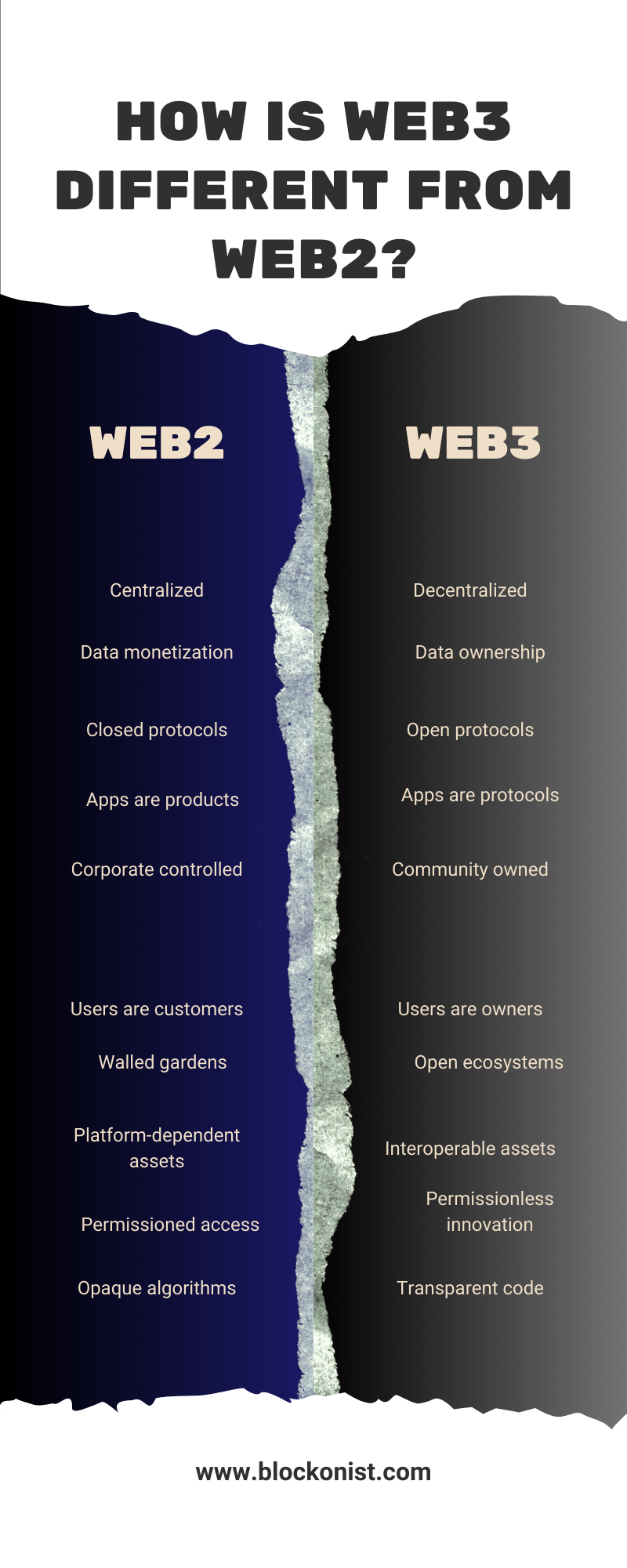
This shift promises to disrupt many digital industries. While Web2 democratized publishing and access to information, Web3 goes further to democratize ownership and economic participation online. Users can own assets, control identity, and collectively shape platform governance. Instead of handing over data to use free services, users can be compensated for their data and attention. Web3 puts users at the center rather than treating them as a product.
The core philosophies behind Web2 and Web3 internet models lead to profoundly different architectures and value distribution. Web3 aims to build a user-owned internet on open protocols and decentralized infrastructure.
In summary:
- Web2 concentrates power in large tech companies that control platforms and user data
- Web3 distributes power among users through open protocols, transparency, and token-based ownership models
- Where Web2 is closed, corporate, and centralized, Web3 aims to be open, community-driven, and decentralized
This shift to user-owned networks underpins the evolution from Web2 to Web3 models. However, in practice there is more of a continuum than a sharp divide between these web eras.
Key Components of Web3
Web3 is made up of several key components and technologies working together:
Blockchain
At the heart of Web3 is blockchain technology. A blockchain is a distributed digital ledger that records transactions in a verifiable and permanent way. Blockchains are the foundation for cryptocurrencies as well as smart contracts and other decentralized applications.
In Web3, blockchains allow digital assets and data to be stored and transacted without any central authority. Some of the most well-known blockchains used in Web3 projects include Ethereum, Solana, Polkadot, Cosmos, and Cardano.
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ether provide the native currency used on blockchains. Cryptocurrencies allow for decentralized financial transactions and new economic models where users can pay for services directly without any intermediaries.
Wallets
Cryptocurrency wallets are software programs where users can store the private keys to their cryptocurrency holdings as well as interact with blockchain-based applications. Wallets are essential for accessing Web3 services and platforms.
Popular Web3 wallets include Metamask, Coinbase Wallet, WalletConnect, Slope, and Rainbow.
Decentralized Apps (dApps)
Decentralized apps (dApps) are applications built on top of blockchain networks. Because they eliminate centralized intermediaries, dApps allow users greater control over their data and digital assets.
Existing dApps cover areas like finance (lending, trading), gaming, identity systems, cloud storage, and more. dApps can also take the form of DAOs.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
DAOs are a new form of decentralized governance and organization. DAOs are community-led entities with rules encoded into smart contracts on the blockchain. This replaces the need for centralized management and creates a structure where decision-making power belongs to token holders.
Prominent DAOs include MakerDAO, AAVE, and dxDAO. DAOs manage collective resources from treasuries to protocols.
Decentralized Storage
Decentralized storage solutions allow data to be stored in a distributed network rather than centralized servers. This provides greater security, transparency, and user control. Projects like Filecoin, Storj, and Arweave enable decentralized storage for Web3 apps.
Oracles
Oracles are third-party services that provide external data to blockchains and smart contracts. This could include information like weather data, election results, sports scores, etc. Oracles are needed for many real-world use cases.
Chainlink is the most widely used oracle network for delivering data to different blockchains.
Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work and proof-of-stake are how blockchains can validate transactions and achieve agreement without a central party. These algorithms allow decentralized networks to ensure accuracy and security.
Bitcoin and Ethereum currently use proof-of-work while newer blockchains are transitioning to less energy-intensive methods like proof-of-stake.
Identity Management
Decentralized identity management gives users control over their digital identities and data. Rather than identities being tied to accounts on centralized platforms, Web3 identity systems use cryptography and blockchain to prove identity in a privacy-preserving and self-sovereign way.
SelfKey, Civic, and Blok are some of the major Web3 identity projects.
Key Benefits of Web3
The technologies and architecture behind Web3 aim to solve many of the problems associated with today’s centralized internet model. Some of the key benefits include:
- Reduced monopoly power – No single entity controls the entire ecosystem or can dominate markets through data monopolization.
- Censorship resistance – Content cannot be easily removed or blocked because there is no central platform regulating activity.
- Enhanced privacy – User data and identities are not controlled by third parties because interactions happen in a decentralized manner.
- True ownership – Users have actual ownership of digital assets verified on-chain rather than platform-dependent assets.
- Financial opportunity – New tokenized economic models powered by cryptocurrencies and DeFi allow wider participation.
- Transparency – All transactions and rules are recorded on public blockchains enabling accountability.
- Innovation – Open ecosystems fuel rapid innovation and collaboration rather than walled gardens.
- Accessibility – Everyone has permissionless access to the same underlying protocols to build or contribute.
What are some examples of Web3 in the real world?
Here are some real-world examples of Web3 applications and use cases:
- Cryptocurrency payments – Services like BitPay and Coinbase Commerce allow merchants to accept payment in crypto. This replaces traditional payment rails with decentralized blockchain transactions.
- NFT ticketing – Platforms like Yellowheart are selling event tickets as non-fungible tokens that provide proof of ownership on a blockchain. This prevents fraud and allows tickets to be resold peer-to-peer.
- Supply chain tracking – Businesses can track goods and inventory using the transparency of blockchains. For example, tracking the provenance of diamonds on a ledger.
- Decentralized storage – Filecoin and Storj allow users to rent out spare disk space in a decentralized manner rather than relying on centralized servers.
- DAO organization – Groups like MakerDAO and dxDAO have billions in assets under management while operating through decentralized governance models and proposal voting.
- Identity management – uPort and Civic allow users to control their identity via private keys instead of accounts on platforms. This maintains privacy while still allowing verification.
- Decentralized finance – Platforms like Uniswap and Aave have created an open financial system for trading, lending, and borrowing crypto assets without intermediaries.
- Non-fungible gaming – Games like Axie Infinity integrate blockchain to create scarce digital assets and provably rare game items.
- Metaverse spaces – Decentraland lets users buy virtual land NFTs and build immersive experiences owned and controlled by users rather than a platform.
These represent just some of the growing examples of Web3 adoption across industries.
Challenges Facing Web3 Adoption
While the potential of Web3 is vast, there remain significant challenges and barriers slowing mainstream adoption:
Technological Maturity
Many Web3 building blocks are still developing. Scalability, security, speed, and other technical issues need to be improved before mass adoption is feasible.
User Experience
Current Web3 apps can be difficult and unintuitive to navigate. More work is required to create easy-to-use and seamless user experiences.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Government policy towards cryptocurrencies and decentralized platforms remains uncertain and can hinder development.
Audience Understanding
Most internet users have little understanding of blockchain, crypto, and Web3 limiting participation. Better education is needed.
Platform Resistance
Large tech incumbents may resist or lobby against Web3 models that disrupt their dominance and data control.
Despite these challenges, Web3 advocates believe its foundations are now robust enough for mainstream growth in the 2020s. Ongoing funding and development aim to tackle current limitations.
Examples of Popular Web3 Applications
While still early, a variety of Web3 applications across different categories showcase the technology’s practical use cases:
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- Uniswap – Leading decentralized crypto exchange running on Ethereum
- Aave – Open lending protocol enabling crypto collateralized loans
- MakerDAO – Service for issuing stablecoins backed by crypto reserves
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
- CryptoPunks – Collectible characters minted as NFTs on Ethereum
- OpenSea – Largest NFT marketplace with millions in sales volume
- Axie Infinity – Popular blockchain-based game involving breeding NFT creatures
Metaverse
- Decentraland – 3D virtual world where users buy digital land as NFTs
- The Sandbox – Community-driven gaming metaverse for creating experiences
- Cryptovoxels – Virtual world monetized by selling land parcels as NFTs
Social Networks
- Lens Protocol – Open platform for decentralized social apps built on blockchain
- Indify – Web3 social network for artists and creators with integrated NFT features
- Discord – Leading chat app increasingly used for Web3 communities
This list just scratches the surface but gives a sample of innovative Web3 models. New examples continue to emerge across more industries and use cases.
The Evolution of Web3
Like the early internet, no one can predict exactly how Web3 will evolve – but expectations are high for profound change. Here is one potential vision for how Web3 could reshape society:
Phase 1: Cryptocurrency proliferation (Now – 2025)
- Cryptocurrencies gain mainstream awareness and adoption for payments
- Onramp services make crypto entry easy for average users
- DeFi sees rapid growth with yield opportunities attracting capital
Phase 2: Mass dApp adoption (2025-2030)
- Mature protocols and scalable infrastructure enable dApp explosion
- dApps integrate into society for finance, identity, social, gaming, data storage
- Web3 phones/devices gain popularity as dedicated dApp portals
Phase 3: Cryptoeconomy and culture (2030+)
- The internet becomes a user-owned ecosystem where protocols replace platforms
- Millions participate in decentralized governance of digital spaces
- Creation and innovation thrive in open, transparent environments
- Sectors like art, media, and knowledge shift to Web3 models
- A robust token economy flourishes as more value resides on-chain
- The lines blur between online and offline as web3 and reality converge
This transition may take over a decade. But Web3 promises to reshape the digital landscape in profound ways. While the future is uncertain, its emergence represents an exciting new phase for technology and society.
What are some concerns around Web3?
Here are some potential concerns and criticisms surrounding Web3:
- Overpromising potential – Some believe Web3 is overhyped technology that won’t live up to its promises or radically transform the internet.
- Lack of maturity – Many Web3 technologies are still nascent and have UX issues or limitations to overcome before mainstream use is likely.
- Speculation and volatility – The crypto market sees a lot of speculation which can lead to boom and bust cycles detrimental to adoption.
- Cybersecurity risks – Web3 comes with new cybersecurity challenges including wallet hacks, stolen funds, and Ponzi schemes.
- Threat of overregulation – Governments may overregulate aspects of Web3 in ways that stifle innovation in decentralized systems.
- Tech oligarchy concerns – There are fears that big tech firms may eventually dominate Web3 the way they have Web2 if they control key protocols.
- Environmental impact – Proof-of-work blockchains consume enormous energy. This could prevent mass adoption. Alternatives like proof-of-stake are improving but not yet proven at scale.
- Widening inequality – As with most new technologies, Web3 may initially benefit the affluent and technically savvy more than the general public.
- Legal uncertainty – Open legal questions around jurisdictional authority, liabilities, and regulation of crypto-related technologies.
While Web3 promises many benefits, it also comes with substantial risks, challenges and criticisms that could limit the scale or scope of its impact. Striking the right balance of innovation and regulation will be key.
Frequently Asked Questions About Web3
Is Web3 the same as blockchain?
No, Web3 and blockchain are not the same. Blockchain technology like Bitcoin and Ethereum is a key component of Web3, providing the decentralized digital ledger for applications. But Web3 encompasses many technologies beyond just blockchain.
Is Web3 already here?
Web3 is an evolving concept more than a definitive reality. Many of its components exist but have not yet reached mass adoption. Most agree we are in the early innings as protocols mature and more users transition.
Do I need to buy cryptocurrencies to use Web3?
In most cases, yes – you’ll need a cryptocurrency like Ether to interact with Web3 apps and pay gas fees. But as onramps improve, mainstream users may not even realize they are using crypto.
Is Web3 going to replace the internet?
Web3 will likely augment rather than replace the internet. But it aims to reinvent online infrastructure in a decentralized way. Some Web2 applications may transition models or fade away.
Does Web3 have security risks?
Yes, Web3 comes with risks. Blockchain is secure, but vulnerabilities exist at the contract and app levels. Users must take security precautions around managing private keys and wallet access.
What will Web3 disruption look like?
Potential disruption spans ads, social media, marketplaces, content creation, and digital identity. Incumbents may adapt or new entrants may emerge. But user ownership and open competition will increase.
Who will regulate Web3?
With no centralized control, regulation in Web3 may come through decentralized governance agreed upon by network participants. But governments are still figuring out appropriate policies for cryptocurrency and decentralized platforms.
Is Web3 too complex for average internet users?
Today Web3 has a significant onboarding challenge. But as usability improves and people understand the value, Web3 can reach mainstream adoption like previous internet revolutions.
Conclusion
Web3 represents an ambitious vision to reshape the digital world based on principles like decentralization, transparency, and user empowerment. While technical challenges remain, Web3 has immense potential to restore some of the original open ethos of the internet. This guide provided an introduction to key Web3 building blocks, benefits, current use cases, and future possibilities. How exactly Web3 evolves remains to be seen, but its emergence signifies a new technological frontier with profound implications for economics, governance, and culture.
Raksha, a seasoned journalist, specializes in crafting insightful narratives on blockchain and AI developments. With a keen eye for innovation, she distills complex topics into accessible stories, providing readers with a clear understanding of the dynamic intersection between these transformative technologies.